305. Number of Islands II
Question
You are given an empty 2D binary grid grid of size m x n. The grid represents a map where 0's represent water and 1's represent land. Initially, all the cells of grid are water cells (i.e., all the cells are 0's).
We may perform an add land operation which turns the water at position into a land. You are given an array positions where positions[i] = [ri, ci] is the position (ri, ci) at which we should operate the ith operation.
Return an array of integers answer where answer[i] is the number of islands after turning the cell (ri, ci) into a land.
An island is surrounded by water and is formed by connecting adjacent lands horizontally or vertically. You may assume all four edges of the grid are all surrounded by water.
Example 1:
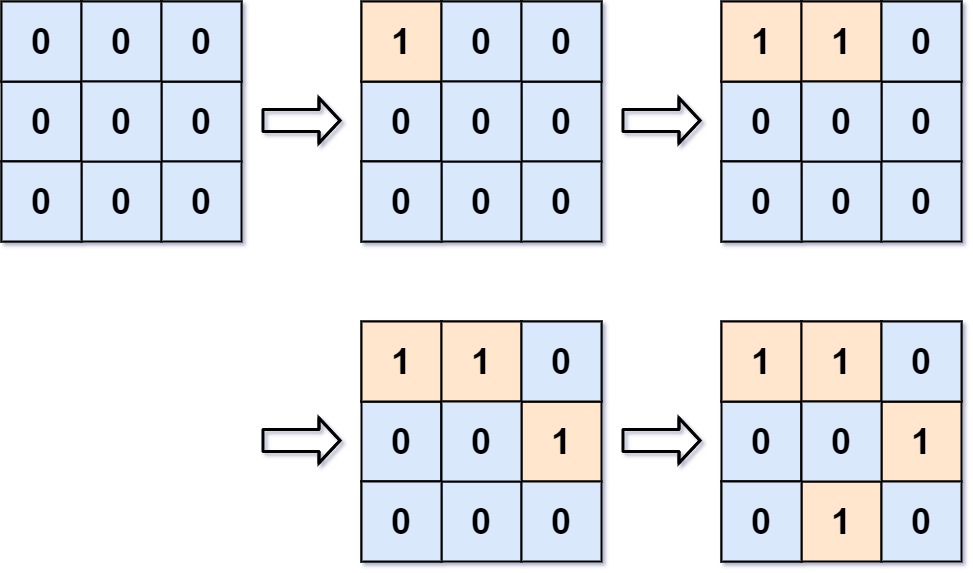
Algorithm
Find the final components count in a forrest.
The point for this question is how you construct the graph(the connection of nodes).
Code
Standard answer
class UnionFind {
int[] parent;
int[] rank;
int count;
public UnionFind(int size) {
parent = new int[size];
rank = new int[size];
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
parent[i] = -1;
count = 0;
}
public void addLand(int x) {
if (parent[x] >= 0)
return;
parent[x] = x;
count++;
}
public boolean isLand(int x) {
if (parent[x] >= 0) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
int numberOfIslands() {
return count;
}
public int find(int x) {
if (parent[x] != x)
parent[x] = find(parent[x]);
return parent[x];
}
public void union(int x, int y) {
int xset = find(x), yset = find(y);
if (xset == yset) {
return;
} else if (rank[xset] < rank[yset]) {
parent[xset] = yset;
} else if (rank[xset] > rank[yset]) {
parent[yset] = xset;
} else {
parent[yset] = xset;
rank[xset]++;
}
count--;
}
}
class Solution {
public List<Integer> numIslands2(int m, int n, int[][] positions) {
int x[] = { -1, 1, 0, 0 };
int y[] = { 0, 0, -1, 1 };
UnionFind dsu = new UnionFind(m * n);
List<Integer> answer = new ArrayList<>();
for (int[] position : positions) {
int landPosition = position[0] * n + position[1];
dsu.addLand(landPosition);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int neighborX = position[0] + x[i];
int neighborY = position[1] + y[i];
int neighborPosition = neighborX * n + neighborY;
// If neighborX and neighborY correspond to a point in the grid and there is a
// land at that point, then merge it with the current land.
if (neighborX >= 0 && neighborX < m && neighborY >= 0 && neighborY < n &&
dsu.isLand(neighborPosition)) {
dsu.union(landPosition, neighborPosition);
}
}
answer.add(dsu.numberOfIslands());
}
return answer;
}
}
This code is my initial code and cannot pass the test case:
3
3
[[0,1],[1,2],[2,1],[1,0],[0,2],[0,0],[1,1]]
I tried use the sum and product of the position[i][j] as the index in union find. But forget the simplest one, i*n+j flatten the matrix. I believe if I make things easier like this, I could have come up with the final answer.
class Solution {
int[][][] parents;
int count;
int[][] grid;
public List<Integer> numIslands2(int m, int n, int[][] positions) {
count = 0;
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (positions == null || positions.length == 0 || positions[0] == null || positions[0].length == 0) {
return res;
}
parents = new int[m][n][2];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
parents[i][j] = new int[]{i, j};
}
}
grid = new int[m][n];
for (int[] position : positions) {
int x = position[0];
int y = position[1];
grid[x][y] = 1;
count++;
union(position, m, n);
res.add(count);
}
return res;
}
private int[] find(int[] position) {
int x = position[0];
int y = position[1];
if (x != parents[x][y][0] && y != parents[x][y][1]) {
parents[x][y] = find(parents[x][y]);
}
return parents[x][y];
}
private void union(int[] position, int m, int n) {
int x = position[0];
int y = position[1];
int[] xRoot = find(parents[x][y]);
if (x-1 >= 0 && grid[x-1][y] == 1) {
int[] leftRoot = find(parents[x-1][y]);
if (xRoot[0] != leftRoot[0] || xRoot[1] != leftRoot[1]) {
parents[xRoot[0]][xRoot[1]] = leftRoot;
count--;
}
}
if (x+1 < m && grid[x+1][y] == 1) {
int[] rightRoot = find(parents[x+1][y]);
if (xRoot[0] != rightRoot[0] || xRoot[1] != rightRoot[1]) {
parents[xRoot[0]][xRoot[1]] = rightRoot;
count--;
}
}
if (y-1 >= 0 && grid[x][y-1] == 1) {
int[] upperRoot = find(parents[x][y-1]);
if (xRoot[0] != upperRoot[0] || xRoot[1] != upperRoot[1]) {
parents[xRoot[0]][xRoot[1]] = upperRoot;
count--;
}
}
if (y + 1 < n && grid[x][y+1] == 1) {
int[] lowerRoot = find(parents[x][y+1]);
if (xRoot[0] != lowerRoot[0] || xRoot[1] != lowerRoot[1]) {
parents[xRoot[0]][xRoot[1]] = lowerRoot;
count--;
}
}
}
}